| 21 |
21. You are given two identical plano-convex lenses, one of which is shown to the right.
When you place an object 20 cm to the left of a single plano-convex lens, the image
appears 40 cm to the right of the lens. You then arrange the two plano-convex lenses back
to back to form a double convex lens. If the object is 20 cm to the left of this new lens,
what is the approximate location of the image?
A. 6.7 cm to the right of
the lens.
B. 10 cm to the right of the lens.
C. 20 cm to the right of the lens.
D. 80 cm to the right of the lens.
E. 80 cm to the left of the lens.
|
|
| 22 |
22. Positive charge Q is uniformly distributed over a ring of radius a
that lies in the y-z plane as shown in the diagram. The ring is centered at the origin. Which of the
following graphs best represents the value of the electric field E as a function of x, the
distance along the positive x axis?
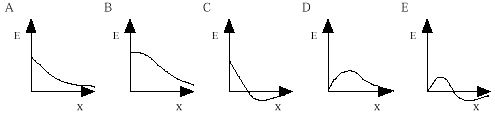
|
|
| 23 |
23. Four point charges are placed at the corners of a square with
diagonal 2a as shown in the diagram.
What is the total electric field at
the center of the square?
A. kq/a² at an angle 45º
above the +x axis.
B. kq/a² at an angle 45º below the -x axis.
C. 3 kq/a² at an angle 45º above the -x
axis.
D. 3 kq/a² at an angle 45º below the +x
axis.
E. 9 kq/a² at an angle 45º above the +x
axis.
|
|
| 24 |
Both questions 24 and 25 refer to the system shown in the diagram. A
spherical shell with an inner surface of radius a and an outer surface of radius b is made
of conducting material. A point charge +Q is placed at the center of the spherical shell
and a total charge -q is placed on the shell.
24. How is the charge -q distributed after it has
reached equilibrium?
A. Zero charge on the inner surface, -q on the outer surface.
B. -Q on the inner surface, -q on the outer surface.
C. -Q on the inner surface, -q+Q on the outer surface.
D. +Q on the inner surface, -q-Q on the outer surface.
E. The charge -q is spread uniformly between the inner and outer surface.
|
|
| 25 |
25. Assume that the electrostatic potential is zero at an infinite
distance from the spherical shell. What is the electrostatic potential at a distance R
from the center of the shell, where b > R > a?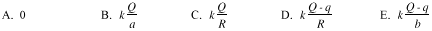
|
|
| 26 |
Use the circuit below to answer questions 26 and 27. B1, B2,
B3, and B4 are identical light bulbs. There are six
voltmeters connected to the circuit as shown. All voltmeters are connected so that they
display positive voltages. Assume that the voltmeters do not effect the circuit.26. If B2 were to burn out, opening the circuit, which
voltmeter(s) would read zero volts?
A. none would read zero.
B. only V2
C. only V3 and V4
D. only V3, V4, and V5
E. they would all read zero
|
|
| 27 |
27. If B2 were to burn out, opening the circuit, what would
happen to the reading of V1? Let V be its original reading when all bulbs are
functioning and let V ' be its reading when B2 is burnt out.A. V ' >
2V
B. 2V > V ' > V
C. V ' = V
D. V > V ' > V/2
E. V/2 > V '
|
|
| 28 |
28. A particle with positive charge q and mass m travels along a path
perpendicular to a magnetic field. The particle moves in a circle of radius R with
frequency f. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?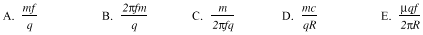
|
|
| 29 |
29. Two wires, each carrying a current i, are shown in the diagram to
the right. Both wires extend in a straight line for a very long distance on both the right
and the left. One wire contains a semi-circular loop of radius a centered on point X. What
is the correct expression for the magnetic field at point X? HINT: The magnitude of the
magnetic field at the center of a circular current loop of radius R is µ0 i/(2R). |
|
| 30 |
30. You are given a bar magnet and a looped coil of wire.Which of the following would induce an emf in the
coil?
I. Moving the magnet toward the coil.
II. Moving the coil away from the magnet.
III. Turning the coil about a vertical axis.
A. I only
B. II only
C. I & II
D. I & III
E. I, II, III
|
|

